Haemorrhoids
Haemorrhoids are never life-threatening. The symptoms of bowel cancer may be like haemorrhoid symptoms. Therefore, it is important to be properly diagnosed.
Most haemorrhoids are treated by non-surgical methods. Minimally-invasive procedures are found to be effective in many patients. Surgery may be needed in advanced cases.
Epidemiology
Haemorrhoidal disease is very common, involving between 4.4% and 36.4% of the overall population. It is a lifestyle disease more common in people with sedentary lifestyle and who take low amount of fibre and fluids in their diet.
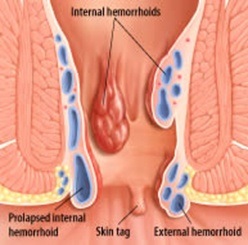
1-External –Below the dentate line
2-internal –Above the dentate line and are painless unless thrombosed.
Pathophysiology
1-Internal Haemorrhoids
Prolapse of normal mucosal cushions containing blood vessels, smooth muscle, and connective tissue. These cushions are located in the left lateral, right posterior, and right anterior regions of the canal (3,7 &11 o clock correlating with the superior rectal artery branches). These cushions play a vital role in fine con
Typical symptom-fresh painless bleeding-bright red are due to arterial source Prolapsing anal mass
 Pruritis
Pruritis
Severity Grading
Haemorrhoids are classified into 4 different types based on their size and how severe they are:
- First degree haemorrhoids often bleed a little bit when you pass a bowel motion, but stay inside the anus and are not usually very painful.
- Second degree haemorrhoids bleed and stick out of the anus when you pass a bowel motion. Once the bowel motion is over, they disappear back inside the anus by themselves.
- Third degree haemorrhoids have to be physically pushed back inside the anus after passing a bowel motion. They may be painful if they are large.
- Fourth degree haemorrhoids are larger lumps that stick out of the anus permanently, and cannot be placed back inside. The blood inside these haemorrhoids may clot and the lumps can become very painful.
- Fifth degree Haemorrhoids – are infected and gangrenous irreducible haemorrhoids
2-External haemorrhoids
Arise in the skin covered lower one-third of the anal canal veins of the external hemorrhoidal plexus
Covered with skin, have cutaneous sensation.
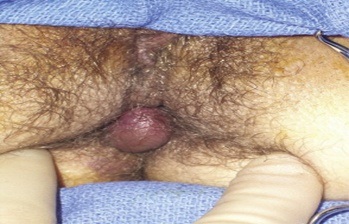
Thrombosed external piles are called perianal haematoma as well
- Caused by spontaneous rupture of one of the external veins
- very Painful
Spray the area with topical Xylocaine spray
- Infiltrate the haemorrhoids with Xylocaine 1% and Ad
- With heavy Mayo scissors, excise the top of the haemorrhoid
- Bathe in salt baths, prn analgesia, regular aperients
Underlying cause:
- Sedentary lifestyle-inadequate fiber
- Constant straining with constipation as well as diarrhea
- Straining during bowel movements
- Sitting for long periods of time on the toilet
- Having chronic diarrhea or constipation
- Being obese
- Having anal intercourse
- Eating a low-fibre diet
- Regular heavy lifting
- Intraabdominal pressure—such as pregnancy, ascites,
- Pelvic tumor-venous outflow reduced
- Portal HTN
Clinical presentation
Symptoms
Signs and symptoms of haemorrhoids usually depend on the type of haemorrhoid.
-External haemorrhoids
These are under the skin around your anus. Signs and symptoms might include: Internal haemorrhoids lie inside the rectum. You usually can't see or feel them, and they rarely cause discomfort. But straining or irritation when passing stool can cause: If blood pools in an external haemorrhoid and forms a clot (thrombus), it can result in: A hard lump near your anus Treatment of Hemorrhoids: Depends on the severity If only bleed only – They are early i.e.: Grade 1 and 2 -Conservative medical, life style modification -Rubber band ligation If prolapse and bleed- They are advanced i.e. Grade 2,3 and 4- -Surgical treatment Eat high-fibre foods.
-Internal haemorrhoids
-Thrombosed haemorrhoids
Treatment Option
Life style advice
- Should drink approximately 6 to 8 (12 oz) glasses of fluid daily.
- Fiber intake should be increased to 25 to 30 grams per day psyllium or hydrophilic colloid are often required
- Most people don't get enough of the recommended amount of fibre — 20 to 30 grams a day — in their diet. Studies have shown that over-the-counter fibre supplements, such as psyllium (Metamucil) or methylcellulose (Citrucel), improve overall symptoms and bleeding from haemorrhoids.
If you use fibre supplements, be sure to drink at least eight glasses of water or other fluids every day. Otherwise, the supplements can cause or worsen constipation.
- Straining and holding your breath when trying to pass a stool creates greater pressure in the veins in the lower rectum.
- Squatting position is better with hip flexed at 30 degrees. This can be achieved by slightly lower toilets or placing a stool under feet while sitting on toilet.
Avoid delaying urge to open bowels
- If you wait to pass a bowel movement and the urge goes away, your stool could dry out and be harder to pass.
Regular exercise.
- Stay active to help prevent constipation and to reduce pressure on veins, which can occur with long periods of standing or
- Exercise can also help you lose excess weight that might be contributing to your haemorrhoids.
- Walking daily up till 30 minutes /day is a good start. This helps with bowels to move and stay active
Avoid long periods of sitting.
- Sitting too long, particularly on the toilet, can increase the pressure on the veins in the anus.
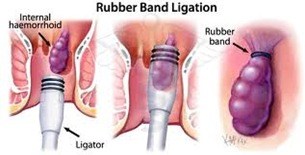
Rubber Band Ligation of Haemorrhoids
- More effective grade 2 and early grade 3 internal haemorrhoids
- May be followed by pain for up to 48 h but Infection and life-threatening hemorrhage uncommon risks
- It is more successful than sclerotherapy for the treatment of hemorrhoids and is well-tolerated procedure
- The complication rate of rubber band ligation is less
- Minor bleeding and vasovagal reaction can occur immediately after the procedure
- If patient experiences pain – band has been applied too low and may need to be removed
- Pain developing in 1 – 2 days may be due to ischaemia
- Relief with analgesia and metronidazole
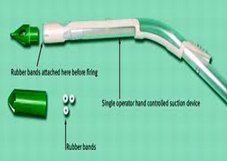
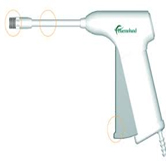
Injection Sclerotherapy
Injection sclerotherapy
- No advantage over the administration of fibre supplements
- Serious side-effects
- Pelvic cellulitis
- Necrotizing fasciitis
- Chemical prostatitis
- Impotence
5% phenol with 0.5% menthol (oily phenol BP)
- Insert needle into submucosa at the anorectal junction
- 3 – 5mL into submucosa at each site
Surgical Treatment
1-Standard Haemorrhoidectomy
2-Staple Haemorrhoidectomy
3-Ligasure Haemorrhoidectomy
4-HALRAR
Surgical treatment for grade III and IV hemorrhoids and is superior to any proposed conservative procedure
But pain is an issue esp.
- Post-operative pain
- Pain on defecation
- Prolonged sphincter spasm
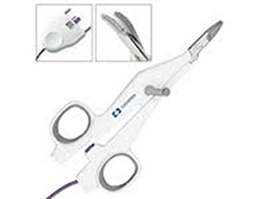
-Ligasure Haemorrhoidectomy
Ligasure is a new energy device that uses precisely calculated and focused energy delivery to achieve the desired tissue effect.
It uses minimal amount of energy to cut tissue, resulting in less collateral damage to surrounding tissues and it cuts and coagulates and seal tissue at the same time,
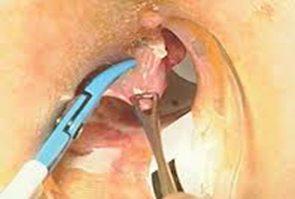
-Staple Haemorrhoidectomy
Circular stapling device resects a strip of mucosa from above the dentate line
It has significant reduction in post-operative pain and is faster procedure
BUT---------
-Treats only internal haemorrhoids
-Can have Serious complications
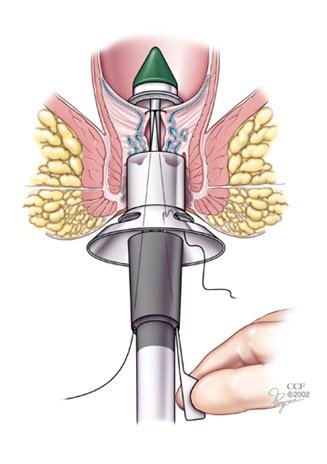
Staple Haemorrhoidectomy Trials
29 RCT -2055 patients
Staple group had higher rate of recurrence
Shorter hospitalstays and faster return to work in staple group
Same complication rate
Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials comparing stapled haemorrhoidopexy with conventional haemorrhoidectomy.
Shao WJ, Li GC, Zhang ZH, Yang BL, Sun GD, Chen YQ - Br J Surg - Feb 2008;
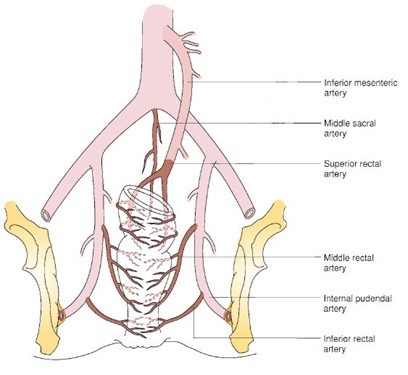
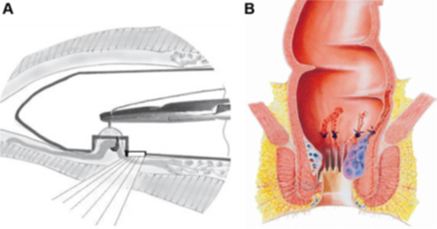
-HALRAR
Doppler ultrasound probe to identify terminal branches of superior haemorrhoidal
artery which are suture ligated through a slit proctoscope
This is Suture only haemorrhoidectomy and no resection is performed.
It is mini-invasive, with low morbidity, and satisfactory short- and medium-term functional results
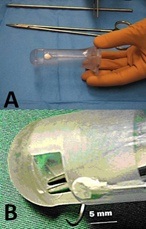
The instrument used consists of an HALTM probe, a transparent resectoscope, provided with a centimetre-sized window at its end through which the ligations are performed. Resectoscope has light source.
A Doppler transducer, connected to the hand-held Doppler apparatus, is found at the base of this window
Take Home Message
-Do not assume that blood in stools is due to haemorrhoids. It needs to be investigated as bowel cancer can present with similar symptoms.
- Do not self-medicate and always see your doctor if having haemorrhoid symptoms
-Haemorrhoids do not lead to cancer.
-Healthy lifestyle with regular exercise and having regular home cooked meals and drinking plenty of oral fluids is simple but an effective preventive strategy