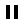Pilonidal Sinus
The word pilonidal is derived from the Latin wordspilus mean ‘hair’, and nidus means ‘nest ‘
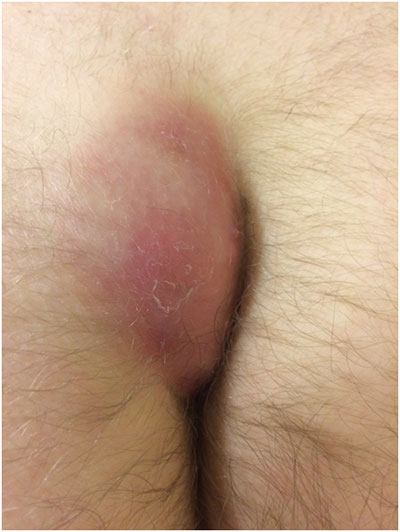
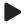
This describes as a spectrum of clinical presentations ranging from symptomatic hair containing cysts and sinuses, to large symptomatic abscesses in the sacrococcygeal region that have tendency to recur.
The term pilonidal sinusis described back as far as 1833 when Mayo described a hair containing cyst which was located below the coccyx.
Epidemiology
Incidence is about 26 per 100,000population and it is more common in males with M:F ratio of 4-1. It mainly occurs in Caucasians in late 19s to early 20s decreasing after 25.
Other risk factors also play role such as:
- Positive family history,
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Obesity.
Pathophysiology
The exact cause is unknown but it seems to be a combination of factors such as:
- Changing hormones,
- Hair growth and
- Friction from spending a long time sitting.
Activities that cause friction such as sitting down forlong andhair growing and getting buried under the skin especially the weaker skin in natal cleft. The body considers the hair as foreign body and launches an immune response. This immune response forms cyst around the hair. If not treated, a pilonidal cyst can lead to an abscess or sinus cavity.
Clinical presentation
The condition may present as:
- An abscess or
- Pain and purulent discharge from chronic pilonidal sinus.
Lots of patients present first time with a painful fluctuant abscessin the sacrococcygeal region.
About 50% of the patients present with anabscess. Pain and purulent discharge are present in 70% of the time.
Diagnosis
A diagnosis is made by clinical examination and inspection of the sacrococcygeal region by the clinician.
Treatment Options
The treatment depends on clinical presentation and symptoms such as inflammation, abscess or purulent discharge. There are three main categories with which the disease present such as an acute pilonidal abscess, chronic pilonidal disease and recurrent pilonidal disease. Surgical treatment is tailored depending on presentation.
- Non-surgical treatment
One of the simplest medical treatments is shaving the area free of hair by using laser hair removal treatment.
If the case is diagnosed early on, and pain is not that severe, non-surgical treatments may help. Some non-surgical treatments include:
- Antibiotics – Antibiotics treat a wide range of bacteria and help to give relief from infection and discomfort. Painkillers like paracetamol and anti-inflammatory are also provided to reduce pain and swelling.
- Phenol injection – In this treatment, local anaesthesia is given, and then 80% phenol injections are inserted. This procedure is repeated several times. This is not commonly used option now a days.
- Surgical treatment
Surgical treatment is a main treatment if symptoms are recurrent. The treatment depends on clinical presentation.
- Incision and drainage – This surgery is performed for large or repeatedly infected snus. The sinus is cut, and all the pus and debris are removed. After completion of the process, the wound is closed by stitching.
- Endoscopic ablation – An endoscope is used and inserted into the sinus cavity Then hair and infected tissues are removed, and sinus is cleaned with a solution.
- Innovative techniques; There are some new innovations in the treatment but they are still being studied such as fibrin glue, radio frequency ablation and laser ablation.
- Excision and a flap repair are the gold standard of treatment – Plastic surgery is considered an option if the area being treated is large. In this case, sinus is removed, and the affected skin is reconstructed. I perform a rotation flap called Limberg flap repair which has got a high success rate and very low wound breakdown issues.