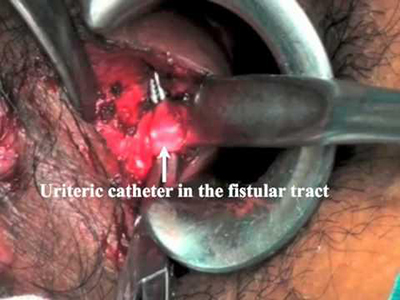
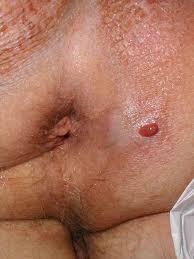
Fistula in Ano
Definition:
- Hollow tract lined with granulation tissue connecting a primary opening inside the anal canal to a secondary opening in the perianal skin
- Common condition-prevalence 1:10,000
- Males-4th decade
What are Causes:
- History of an abscess-about 50% of anal abscess lead to anal fistula
- Crypto glandular theory 90%: Anal canal glands at the dentate line afford a path for infecting organisms to reach the intramuscular space
- Crohn’s dsease-35% of pts with CD -perianal fistula as first presentation
- Radiation
- TB
- Actinomycosis
What is Differential diagnosis
- Pilonidal infection
- Hidradenitis suppurativa
- Crohn’s disease
- Tuberculosis
- Intrapelvic sepsis
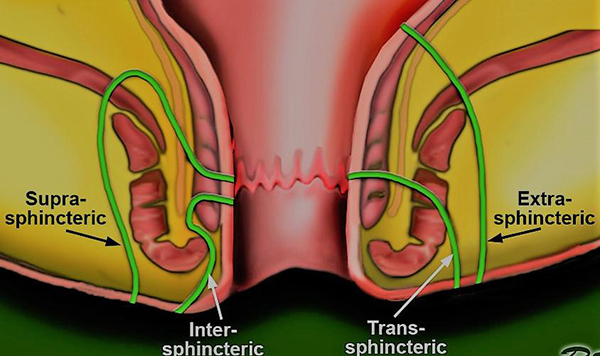
What are types of Anal Fistulae – (Parks classification)
4 Types of fistulae:
- A-Inter-sphincteric -70%
Common course - Via internal sphincter to the inter-sphincteric space and then to the perineum
- B-Trans-sphincteric-25%
Common course - Low via internal and external sphincters into the ischiorectal fossa and then to the perineum
- C-Supra-sphincteric -5%
Common course - Via inter-sphincteric space superiorly to above puborectalis muscle into ischiorectal fossa and then to perineum
- D-Extra-sphincteric
Common course - From perianal skin through levator ani muscles to the rectal wall completely outside sphincter mechanism
Only 1 % of all anal fistulae
What is Surgical Management
- Depends on if low or high fistula and whether it is simple or complex fistula
- If asymptomatic-not treated but still needs EUA . But of patient is immunocompromised-treated even if asymptomatic
- If diagnosed at time of drainage of perianal abscess and it is low -can be layed open otherwise wait untill tract mature
- LAY OPEN-only if simple and low
If complex
- SETON PLACEMENT
- FIBRIN GLUE
- MESH PLUG
- ADVANCEMENT RECTAL MUCOSAL FLAP
- LIFT
- COLOSTOMY
What Investigations are needed
- MRI
- Anorectal USS
- CT scan
- EUA
What are principles of surgical treatment
- Location internal opening
- Location external opening
- Closure of the primacy tract
- Closure of the secondary tract
- Assess sphincter involvement
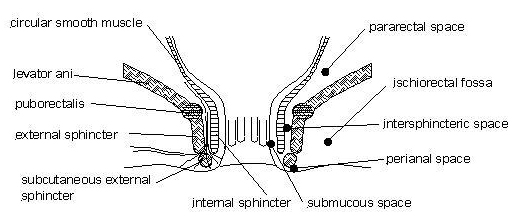
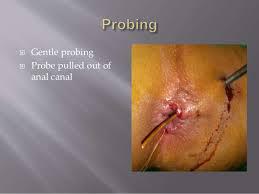
Laying Open Fistula
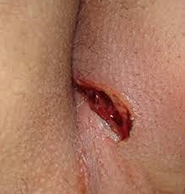
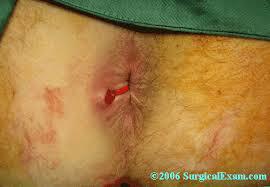
Seton Placement
- Setons keep fistula tract open and prevent recurrence of abscess
- Reserved for high fistula
- Control the sepsis and granulate the tract
- Commonly are draining type setons to prevent tract closing and forming abscess
- Stay in for 3 months and again change or do partial fistulotomy
- Can be uncomfortable
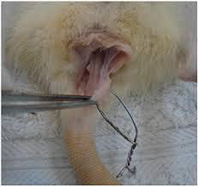
Biological Mesh Plug
- Usually bovine or porcine –can be human
- Treated –sterilized and disinfected collagen –intestinal mucosa
- Induce granulation tissue
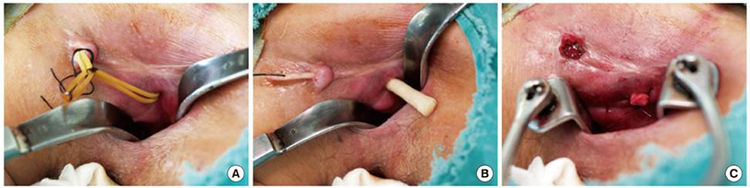
Fibrin Glue
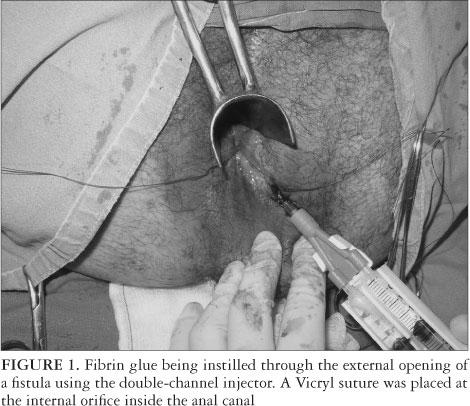
- SUCCESS RATE -50%
- Not very popular
LIFT-ligation of fistula tract